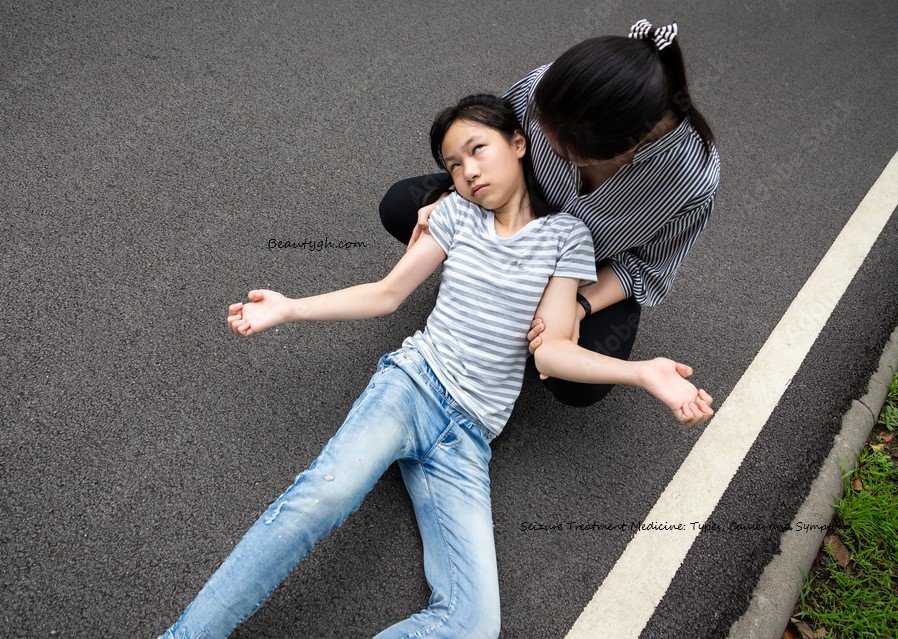
Seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled bursts of electrical activity in the brain ( nerve cells or neurons) that can affect behavior, movements, feelings, and consciousness, such as: twitching or limpness and stiffness.
What causes seizures? |
There are many possible causes of seizures, some of which are more common in adults than in children.
Some seizures have no known cause and may occur only once in a lifetime.
⦁ Medical conditions such as Epilepsy: This is the most common cause of seizures, and it is a neurological disorder that causes recurrent seizures. The exact cause of epilepsy is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
⦁ Brain infections: such as meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, or cerebral malaria.
⦁ Metabolic imbalances: Imbalances in electrolytes, blood sugar, or other chemicals in the blood can cause seizures. ⦁ Brain tumors, which can trigger seizures by causing pressure, bleeding, or inflammation in the brain. |
⦁ Stress: Stress can trigger seizures in some people.
⦁ Traumatic brain injury, which can damage brain tissue or disrupt neurotransmitter activity.
⦁ Substance use or withdrawal, especially from antidepressants, cocaine, methamphetamine, tramadol, or alcohol.
⦁ Stroke, which can cause seizures by reducing blood flow to the brain or causing bleeding in the brain
⦁ Certain medications: such as diphenhydramine, isoniazid, or antibiotics, which can lower the seizure threshold or interact with other drugs. ⦁ Electrolyte imbalance: such as low sodium, calcium, or magnesium levels, which can affect the electrical activity of the brain cells |

Symptoms of seizure:
⦁ Involuntary muscle movements: (jerking, twitching, or stiffening of the body).
⦁ Temporary confusion or loss of awareness
⦁ Changes in behavior: This can include repetitive movements, such as lip smacking or blinking, or sudden changes in mood or activity.
⦁ Sensory changes: This can include seeing, hearing, or smelling things that aren't there, or feeling tingling or numbness. |
⦁ Psychological symptoms such as fear, anxiety or deja vu
⦁ A staring spell or blank look
⦁ Unusual sensations or thoughts: such as fear, hallucinations, anxiety or deja vu (These are warning signs that a seizure is about to occur).
⦁ Emotional changes: This can include feeling sudden fear, anger, or joy. ⦁ Cognitive changes: This can include difficulty thinking, speaking, or understanding what is happening around you. |